Harnessing Wind Power, How Wind Energy Works and Its Impact
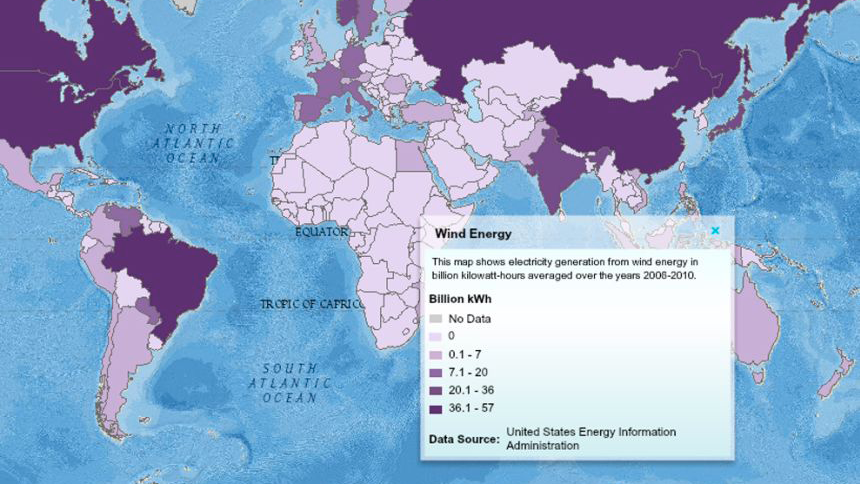
Wind energy, derived from the movement of air, has been a source of power for centuries. Today, wind turbines, towering structures with rotating blades, capture this energy and convert it into electricity. Let’s explore how wind energy works, its advantages, challenges, and impact.
How Wind Energy Works:
Wind turbines, both horizontal-axis and vertical-axis, are the main tools for generating wind energy. Horizontal-axis turbines, with their large blades rotating parallel to the ground, are the most common. They face the wind, and as the blades spin, they turn a generator, producing electricity. Vertical-axis turbines have varied, circular blades that rotate around their tower, allowing for easier maintenance.
Wind farms, consisting of hundreds of turbines, are often constructed to generate large amounts of electricity. These farms can be onshore or offshore, taking advantage of strong and consistent winds. They’re usually located in agricultural areas, where land between turbines can still be used for farming.
Advantages of Wind Energy
Renewable and Clean: Wind is an abundant and clean source of energy, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing air pollution.
Cost-Effective: Wind energy is relatively inexpensive, making it a viable option for both developed and developing economies.
Global Accessibility: Wind turbines can be installed almost anywhere, providing energy in remote areas and contributing to economic development.
Job Creation: Wind energy projects create job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, supporting local economies.
Challenges of Wind Energy
Initial Cost: Setting up wind farms and installing turbines requires significant investment, although operational costs are low.
Land Use and Habitat Impact: Wind farms may compete with other land uses, such as agriculture, and disrupt wildlife habitats.
Wildlife Concerns: Wind turbines can pose risks to birds and bats, requiring mitigation measures to minimize impacts.
Offshore Challenges: Offshore wind farms may affect marine ecosystems and require careful planning to minimize environmental impacts.
Transmission Issues: Wind-rich areas are often remote, necessitating the construction of transmission lines to deliver electricity to urban centers.
Impact of Wind Energy
Economic Growth: Wind energy contributes to economic growth by creating jobs, stimulating investment, and reducing energy costs.
Environmental Benefits: Wind power reduces greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, improving air quality and mitigating climate change.
Energy Security: Diversifying energy sources with wind power enhances energy security and reduces dependence on imported fuels.
Community Development: Wind projects can provide economic opportunities and infrastructure improvements in rural communities.
Wind energy offers a sustainable solution to meeting energy needs while mitigating environmental impacts. By addressing challenges and maximizing benefits, wind power can play a significant role in the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Related News
Royal College welcomes its new Principal – Mr.Athula Wijewardena
Royal College welcomes its new Principal, Mr. Athula Wijewardana. With a distinguished career in educational leadership, Mr. Wijewardana brings a wealth of…
Read MoreNavigating the Future: Essential Skills for the Workforce in 2030
As we navigate the rapidly evolving job market, understanding which skills will become essential in the coming years is vital for both…
Read MoreFrom Different Eras to the Era of AI
It only took five to six decades for humanity to reach its current state. The transition from the industrial period to the…
Read MoreFeel The Beat of A Medical Doctor
An Unforgettable Experience! On the 15th of March 2025, the Lanka Hospital Auditorium came alive with the rhythm of medical excellence as…
Read MoreMaster’s Degree any student can do and they are in High Demand
In today's rapidly evolving global job market, Sri Lankan students have a unique opportunity to enhance their career prospects by pursuing master's…
Read MoreCourses
-

IMC – Bachelor of Psychology
IMC Education Overview IMC Campus in partnership with Lincoln University College (LUC) Malaysia offers Bachelor of Psychology Degree right here in Sri… -

ANC – BA (Hons) International Business Management (Top-Up)
ANC Education Overview Designed in partnership with public and private business organizations, this program develops one’s ability to critically evaluate business models… -

IIT – BSc (Hons) Computer Science
IIT Campus Overview BSc (Hons) Computer Science provides a solid foundation and training regarding the fundamentals of the computer science field, along… -

APIIT – BSc (Hons) Cyber Security
APIIT Sri Lanka Overview Our BSc (Hons) Cyber Security award is designed to launch your future career in the protection of software… -

ICBS – BSC (Hons) Business Management with Marketing Management
ICBS Overview The BSc (Hons) Business Management with Marketing program, awarded by Queen Margaret University (QMU), is a highly regarded degree that… -

UTS – Diploma of Science
UTS College Sri Lanka Overview The Diploma of Science is designed to empower you to apply scientific thinking and analysis to important… -

CSA – Master of Architecture and Environmental Design
City School of Architecture Overview The Master of Architecture and Environmental Design Degree at CSA is awarded by the University of the… -

APIIT – BSc (Hons) International Business Management
APIIT Sri Lanka Overview Increasingly businesses are becoming more and more international. This requires business management professionals to have knowledge, skills and… -

IIT – BSc (Hons) Artificial Intelligence And Data Science
IIT Campus Overview The BSc (Hons) Artificial Intelligence and Data Science course is awarded by Robert Gordon University (RGU) in the UK… -

ICBS – International Degree Foundation in Business / IT
ICBS Overview The Scottish Qualification Authority (SQA) is a globally recognized organization dedicated to education and qualification development. SQA is responsible for… -

APIIT – BA (Hons) Finance and Business Enterprise
APIIT Sri Lanka Overview Finance and accounting are no longer just about taxation and the management of financial capital. This award will… -

APIIT – MBA General
APIIT Sri Lanka Overview The MBA is awarded by Staffordshire University, UK. This award is an advanced course of study in management… -

ANC – LLM in International Business & Commercial Law
ANC Education Overview This course is designed for graduates of law, business and finance in a legal or a corporate job role… -

AOD – BA (Hons) Fashion Design and Marketing
Academy of Design Overview The syllabus is from the UK’s Northumbria University, as one of their most revered flagship programmes and is… -

APIIT – MSc. Marketing Management
APIIT Sri Lanka Overview This MSc Marketing Management degree – awarded by Staffordshire University, UK is an advanced course of study in…
Newswire
-

Heavy rainfall above 100 mm expected in some provinces today
ON: April 7, 2025 -

Welikada OIC faces transfer over suspect’s death in police custody
ON: April 6, 2025 -

NPP MP Kosala Nuwan (38) passed away
ON: April 6, 2025












